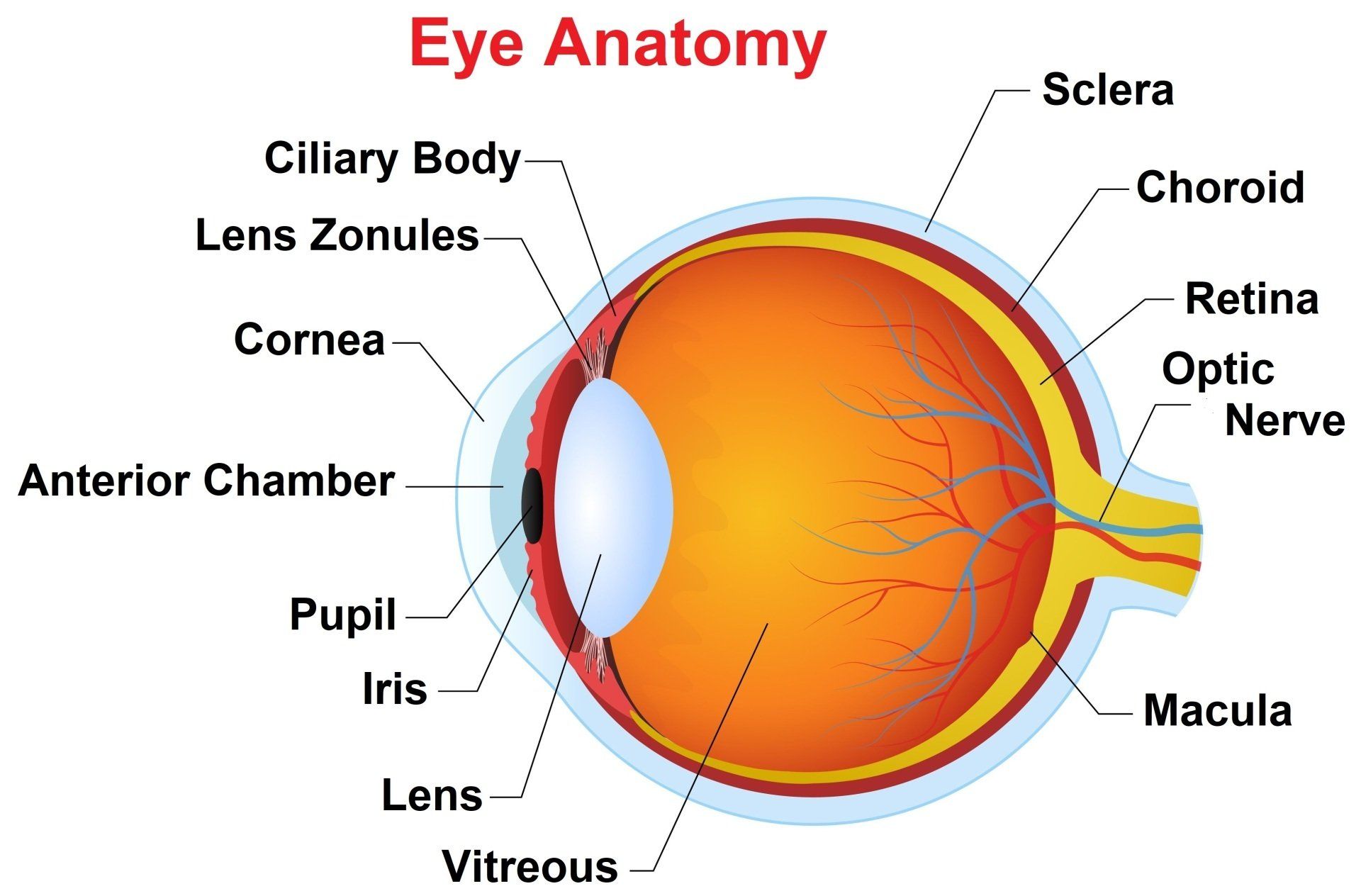
Eye Anatomy
Cornea-the transparent dome over the colored portion of the eye, it is the main refractive component of the eye
Sclera-the strong white outer covering of the eye, it provides structure to the eye
Anterior Chamber-fluid filled space located between the cornea and iris
Iris-muscle like structure that regulates the amount of light reaching the retina, gives the eye its color
Pupil-space at the center of the iris where light enters the back of the eye
Lens-structure behind the iris that continues to focus light on the retina, responsible for accommodation (focusing)
Lens Zonules-string like structures attached to the lens that puts tension on the lens to change its shape when focusing
Ciliary Body-muscle involved in focusing the lens and secretes aqueous
Retina-sensory layer at the back of the eye that detects light
Choroid-vascular supply that provides nutrients and oxygen to the retina
Macula-central part of the retina associated with our detailed vision, has a higher concentration of cones
Optic Nerve-takes signals of light from the retina back via the visual pathway to the brain